Loose Connective Tissue Outside The Muscle
The endomysium is the connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber cell.
Loose connective tissue outside the muscle. Dense connective tissue helps attach muscles to bones and link bones together at joints. The epimysium encircles all the fascicles to form a complete muscle. The perimysium encircles a group of muscle fibers forming a fascicle. The individual myocyte is ensheathed by endomysium which consists of collagen types iii and iv.
Specialized connective tissue encompasses a number of different tissues with specialized cells and unique ground substances. The key difference between connective tissue and muscle tissue is that the main function of connective tissue is to provide a connection between tissues organs and other body parts while the main function of the muscle tissue is to carry out movements of the body. Connections between the extracellular matrix and muscle cells are facilitated by focal adhesions via dystrophin and integrin. The collagen fibres of these connective tissue wrappings merge with the tendons aponeuroses or periosteum the dense connective tissue structures that link the muscle to bone on which the muscle pulls.
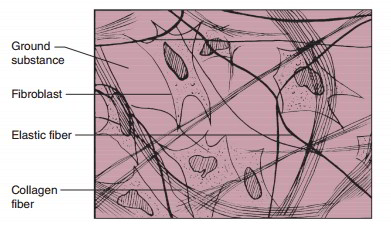
The loose connective tissue found outside the muscle organ that forms flexible sticky packing material between muscles bones and the skin. Each muscle fibre is surrounded by loose connective tissue and these contain capillaries and nerve fibres. The dense irregular connective tissue has a dense woven network of collagen and elastic fibers in a viscous matrix. Dense connective tissue is found in joint capsules muscle fascia and the dermis layer of skin.
This connective tissue covering is known as the endomysium endon greek for within. Where the muscle attaches to the stationary bone. Dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to the bone. Fibers are tapered at each end and have a single nucleus nonstriated muscle fibers fascia the loose connective tissue outside the muscle organs that forms a flexible sticky packing material between muscles bones and the skin.
A tendon is a cordlike extension of the preceding three linings. Fascia is loose connective tissue that surrounds and interpenetrates all components of the human body including muscles nerves blood vessels and organs. It provides structural integrity serves as a matrix for intercellular communication and is involved in biochemical and bioelectric signaling. Striated muscle communicates with the surrounding connective tissue.


















